Defect Description
Long, hollow capillaries in glass filaments that provide pathway for conductive filament formation [1-2].
Defect Formation Process(s)
Air bubbles in molten glass are drawn into long capillaries in glass filaments during the processing of E-glass (most common fiberglass used in the electronics industry) [1-2].
|
List of Tests to Precipitate this Defect |
Failure Acceleration |
Likelihood to Precipitate this Defect (condition) |
Failure Mechanism(s) |
|
Temperature, Humidity and Bias |
• Humidity and high temperature increases moisture absorption by the laminate materials that accelerates filament growth [3] • Voltage gradient accelerates filament growth [3] |
✔ |
• Conductive Filament Formation |
|
Hot Step Stress |
• High temperature increases the moisture absorbed by the laminate materials given a threshold moisture content [3] |
✇ (The presence of threshold moisture content in the laminate materials) |
|
|
Thermal Shock |
• Same as Hot Step Stress |
✇ (Same as Hot Step Stress) |
|
|
Combined Environment |
• Same as Hot Step Stress |
✇ (Same as Hot Step Stress) |
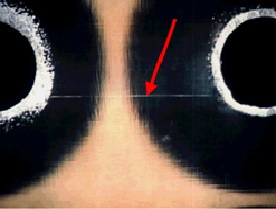 [4]
[4]
References
[1] Pecht M., Hillman C., Rogers K., and Jennings D., “Conductive filament formation: a potential reliability issue in laminated printed circuit cards with hollow fibers.” IEEE Transactions on Electronics Packaging Manufacturing, vol.22, no.1, pp.80-84, 1999.
[2] Rogers K., Hillman C., Pecht M., “Hollow fibers can accelerate conductive filament formation.” ASM International Practical Failure Analysis, vol.1, issue 4, pp. 57-60, 2001.
[3] Rudra B., Pecht,M., Jennings, D., “Assessing Time-to-Failure Due to Conductive Filament Formation in Multi-Layer Organic Laminates.” IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Techniques- Part B, vol. 17, no. 3, 1994.
Permission for pictures
[4] Rogers K., Hillman C., Pecht M., “Hollow fibers can accelerate conductive filament formation.” ASM International Practical Failure Analysis, vol.1, issue 4, pp. 57-60, 2001.
Top