The Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) and the Department of Electrical Engineering (EE), Syed Babar Ali School of Science and Engineering (SBASSE), at Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS) have recently started a research collaboration in the field of batteries and reliability. This partnership will support the research of Doctoral Students Huzaifa Rauf and Hayder Ali from Lahore University of Management Sciences.
SBASSE is the first private research-focused school of science and engineering in Pakistan and stands out as one of the region’s top schools. Much like CALCE, SBASSE practices a no-boundaries philosophy, which encourages cross-disciplinary collaborations. The school’s impressive scholars and its global collaborations make it a great partner in furthering battery research.
Hayder Ali Huzaifa Rauf

Huzaifa Rauf concentrates on the storage reliability improvement of EVs through machine learning techniques
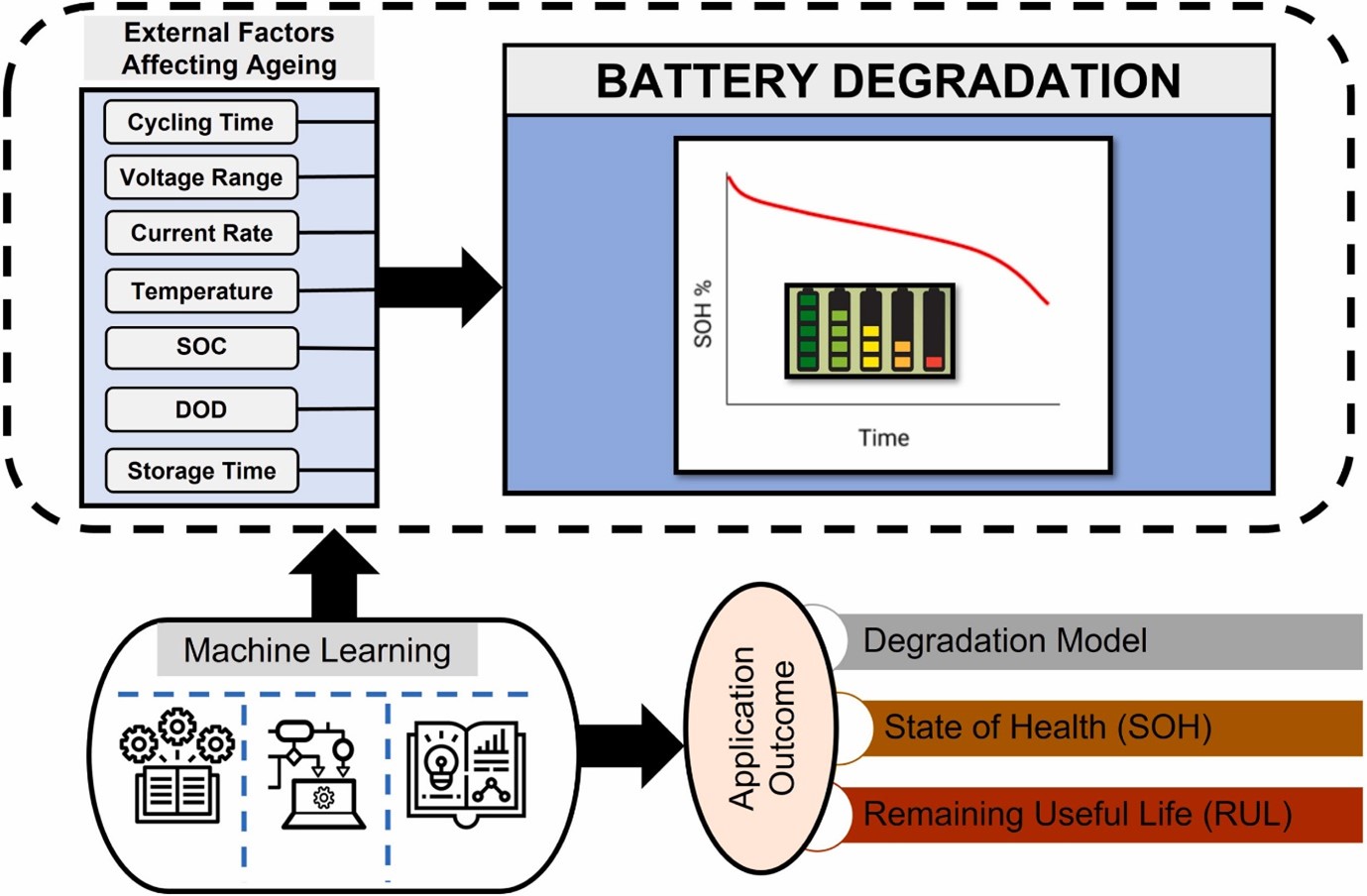 EVs can play a pivotal role in climate change mitigation through the decarbonization of the transportation sector. However, electrical storage is still a bottleneck with many well-documented issues with prevalent Li-ion batteries including environmental degradation, capacity fade, ageing-induced degradation, and end-of-life repurposing. These factors play a pivotal role in the cost of EVs and directly affect their uptake.
EVs can play a pivotal role in climate change mitigation through the decarbonization of the transportation sector. However, electrical storage is still a bottleneck with many well-documented issues with prevalent Li-ion batteries including environmental degradation, capacity fade, ageing-induced degradation, and end-of-life repurposing. These factors play a pivotal role in the cost of EVs and directly affect their uptake.
The current collaboration includes innovative research on the development of accurate estimation models for battery performance, maintenance, prognostics, and health management. It utilizes machine learning (ML) techniques which provide a significant developmental scope to estimate the best parameters and approaches that cannot be identified using conventional techniques. The current strategy includes a non-invasive approach with low computation and high accuracy to model battery degradation.
Hayder Ali concentrates on the Impact of Energy Intensive Apps on in-service Smart Phones
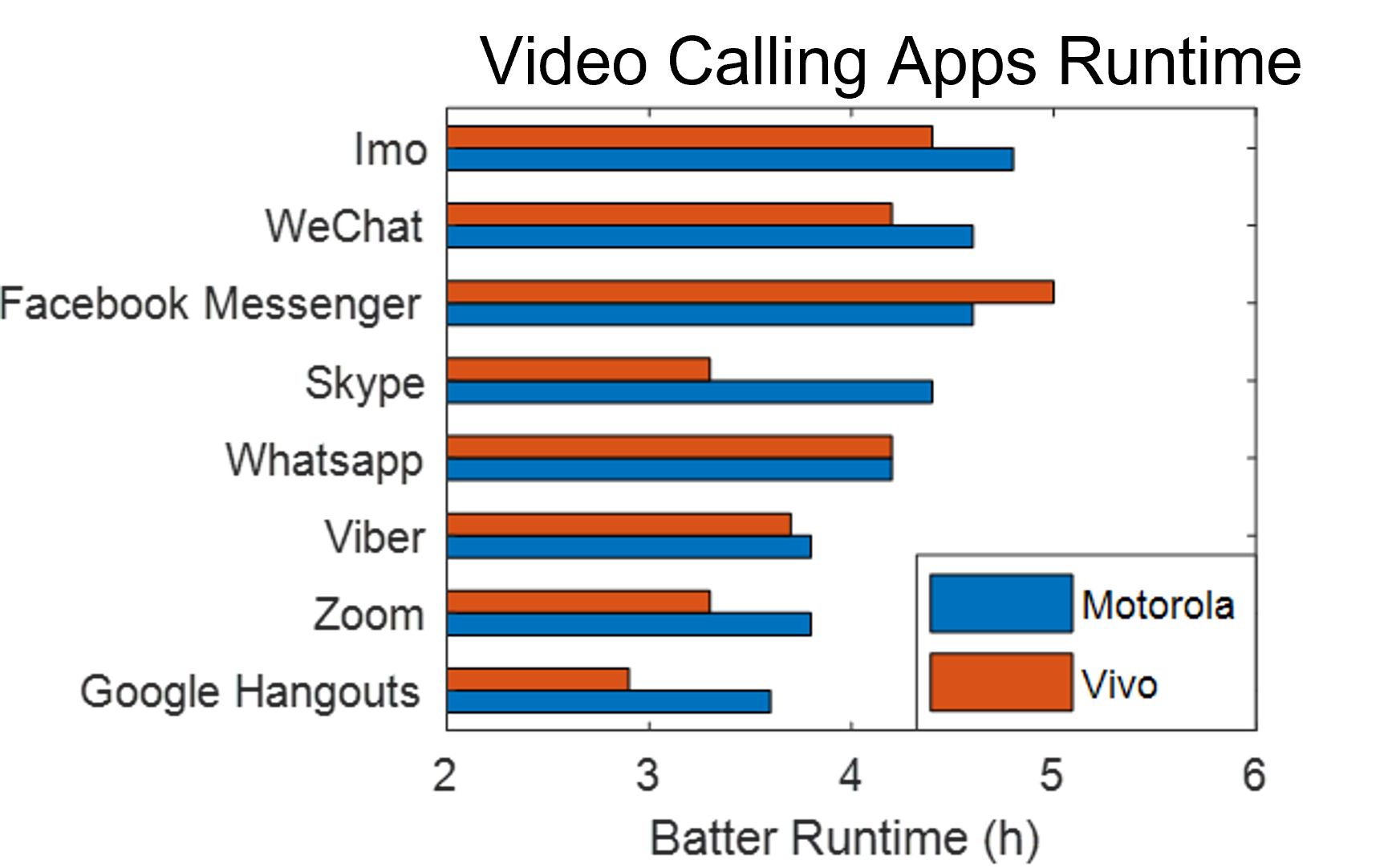 There has been increasing usage of smartphones with energy-intensive apps such as social media, gaming and video conferencing/streaming. For instance, a record 62 million downloads of video calling apps were reported in March 2020. These apps are generally energy-intensive and put a significant strain on the smartphone battery, causing reliability issues such as temperature to rise, resulting in slow operation and sometimes causing unexpected shutdowns. Other battery reliability issues, such as premature shutdown and thermal runaway, may also be seen in certain circumstances.
There has been increasing usage of smartphones with energy-intensive apps such as social media, gaming and video conferencing/streaming. For instance, a record 62 million downloads of video calling apps were reported in March 2020. These apps are generally energy-intensive and put a significant strain on the smartphone battery, causing reliability issues such as temperature to rise, resulting in slow operation and sometimes causing unexpected shutdowns. Other battery reliability issues, such as premature shutdown and thermal runaway, may also be seen in certain circumstances.
It is therefore critical to accurately model the phone performance and reliability during in-service (active) operation and recommend algorithms to improve battery performance. The research focuses on an experimental investigation to measure and evaluate the operational charge/discharge profile, temperature, and terminal voltage of energy-intensive apps and features, such as video calling and gaming, in the in-service operation of various smartphone manufacturers, such as Apple, Samsung, and Vivo. Our research also assesses different apps' short- and long-term effects on smartphone battery life. In addition, the investigation will be done on the influence of the app's algorithm on energy efficiency in terms of operational performance.
Research Articles published in the collaboration between CALCE and LUMS:
-
Preprocessing of Spent Lithium-ion Batteries for Recycling: Need, Methods, and Trends, Hayder Ali, Hassan Abbas Khan, and Michael G. Pecht, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 168, 2022, 112809, ISSN 1364-0321, DOI:10.1016/j.rser.2022.112809
-
Early detection of anomalous degradation behavior in lithium-ion batteries, Weiping Diao, Ijaz Haider Naqvi and Michael G. Pecht, Journal of Energy Storage, vol. 32, p. 101710, December 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101710.
-
An Analytical Model for the CC-CV Charge of Li-ion Batteries with Application to Degradation Analysis, Haining Liu, Ijaz Haider Naqvi, Fajia Li, Chengliang Liu, Neda Shafiei, Yulong Li, and Michael Pecht; Journal of Energy Storage, Vol. 29, June 2020, DOI:10.1016/j.est.2020.101342.
-
Online Degradation State Assessment Methodology for Multi-mode Failures of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, Xiangxiang Liu, Lingling Li, Diganta Das, Ijaz Haider Naqvi, and Michael Pecht; IEEE Access, March 2020, DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2984385.
-
Li-ion Battery Reliability - A Case Study of the Apple iPhone, Yongquan Sun, Lingxi Kong, Hassan Abbas Khan, and Michael Pecht, IEEE Access, Vol. 7, pp. 71131-71141, May 22, 2019, DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2918401.
-
The Effect of Inverter Failures on the Return on Investment of Solar Photovoltaic Systems Tyler Formica, Hassan Abbas Khan, and Michael Pecht, IEEE Access, Vol. 5, September 2017, DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2753246.
-
Circular Economy of Li Batteries: Technologies and Trends, H. Ali, H. A. Khan and M. G. Pecht, August 2021, Journal of Energy Storage, Vol. 40, p. 102690, DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.102690.
-
Evaluation of Li-based Battery Current, Voltage, and Temperature Profiles for In-service Mobile Phones, Hayder Ali, Hassan Khan, and Michael Pecht; IEEE Access, April 2020, DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988728.
For more information about CALCE and the ongoing research projects, please contact Prof. Michael Pecht
Top